Authorities revealed Friday that actor Gene Hackman died of heart disease, with severe Alzheimer’s disease as a contributing factor, a full week after his wife died of hantavirus in their Santa Fe, New Mexico home.
Authorities initially ruled out foul play after the bodies were discovered Feb 26. Chief Medical Investigator Dr. Heather Jarrell said it was possible that Hackman was not aware his wife was deceased in their home.
“Mr. Hackman showed evidence of advanced Alzheimer’s disease," Jarrell said. "He was in a very poor state of health. He had significant heart disease, and I think ultimately that’s what resulted in his death.”
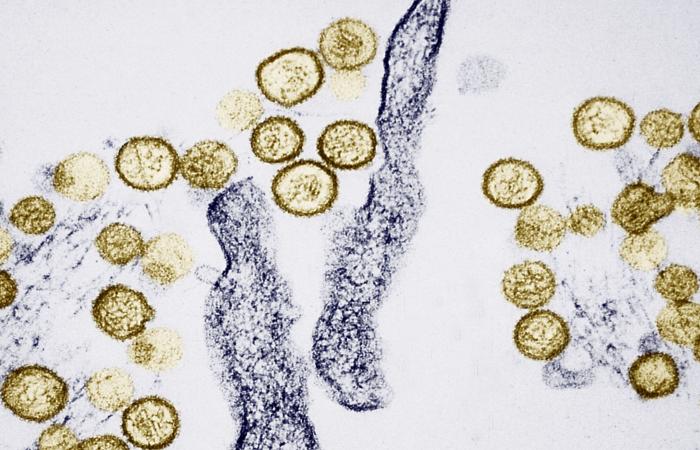
Hackman, 95, was found in the home’s entryway. Meanwhile, his wife Betsy, 65, was found with an open prescription bottle and pills scattered on the bathroom counter. Authorities linked her death to hantavirus pulmonary syndrome, a rare but potentially fatal disease spread by infected rodent droppings.
Below is what you need to know about the hantavirus.
What is the hantavirus?
Hantaviruses are spread by rodents' body fluids and droppings, according to the CDC.
The majority of people who end up with hantavirus do so mostly by breathing in the virus.
Different hantaviruses are found in the United States. Most of these cause hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS), which primarily affect the cardiopulmonary system, according to the CDC.
HPS initially causes flu-like symptoms that can become a more severe illness where people have trouble breathing.
"It's important for people with HPS to begin treatment as early as possible to improve their chances of recovery. HPS is fatal in nearly 4 in 10 people who are infected," according to the CDC.
Non-HPS hantavirus infection can also occur.
Who is at risk of exposure?
Anyone who has contact with hantavirus-carrying rodents, their droppings, urine, saliva or nesting material/area is at risk of HPS, including healthy individuals.
Rodent infestation in and around the home is considered the primary risk for hantavirus exposure.
How does hantavirus spread?
The most common hantavirus that causes HPS in the U.S. is spread by deer mice.
Contracting the hantavirus can take place via different ways:
- Breathe in hantavirus-contaminated air;
- Touch contaminated objects and then touch nose or mouth;
- Are bitten or scratched by an infected rodent;
- Eat food contaminated with hantavirus.
Where do most cases occur?
Cases can occur anywhere. However, they normally take place in rural areas such as forests, fields, and farms. Rodents can get into homes and barns, where they may leave urine or feces.
Although dogs and cats are not known to become infected in the United States, they may bring infected rodents to people or into homes.